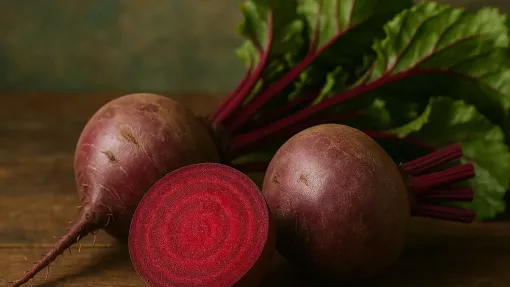Root Vegetables

Root vegetables are a cornerstone of traditional cuisine in many countries. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and natural sweetness, making them a versatile ingredient for everyday meals. Due to their dense structure and ability to hold their shape after cooking, root vegetables are used in soups, stews, casseroles, salads, and even desserts. Learn more about vegetables in the vegetables category.
Different Types of Root Vegetables
Carrots, Beets, Potatoes – A Culinary Classic
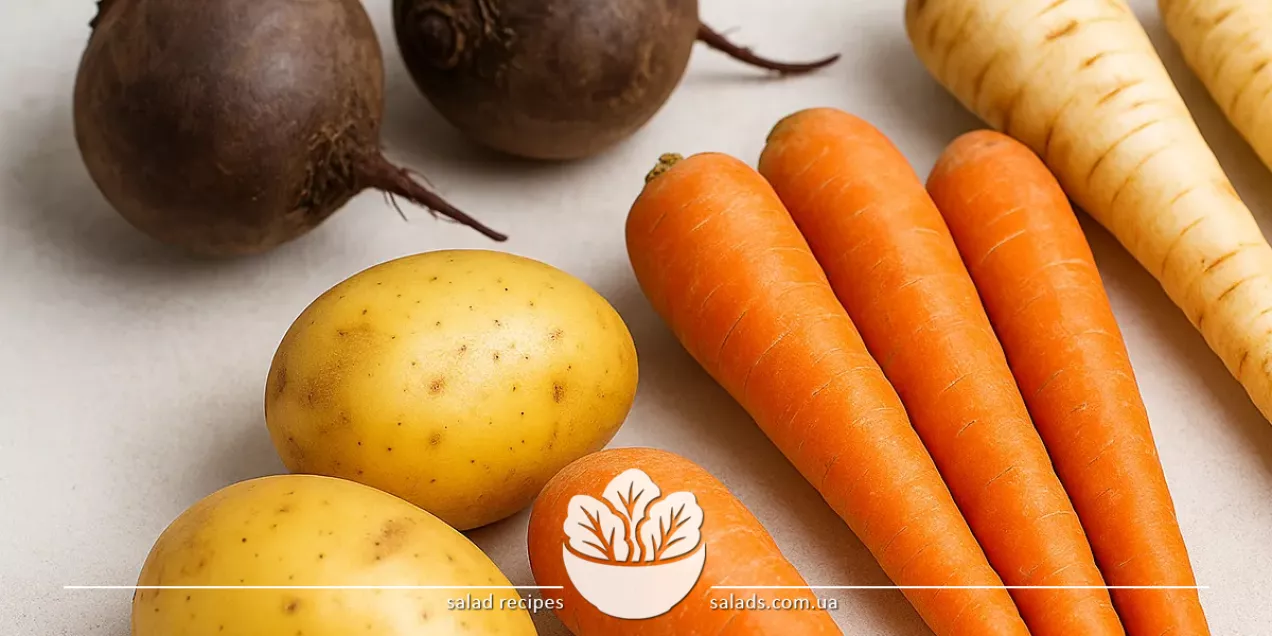
Carrots are among the most common root vegetables, known for their natural sweetness, crunchy texture, and vibrant color. They are used in soups, stews, salads, desserts, and sauces. Carrots can be eaten raw, boiled, baked, or sautéed. They pair well with other vegetables, meats, and fruits. Thanks to their carotene and fiber content, carrots are ideal for a healthy diet. Beets are another classic root vegetable. They are valued for their bright color, earthy aroma, and soft texture after boiling. Beets are the foundation of many traditional dishes, such as borscht, vinaigrette, and salads. They are roasted, stewed, boiled, served with sauces, or as a standalone dish. Beets are also commonly used in modern gastronomy – in smoothies, creams, and casseroles.
Potatoes are a universal ingredient found in cuisines around the world. There are many varieties and cooking methods: boiling, baking, frying, stewing, or mashing. Potatoes are used in soups, casseroles, pies, pancakes, and salads. They pair harmoniously with vegetables, meat, fish, cheese, and herbs. Potatoes are an affordable and nutritious food that easily adapts to any recipe. All three root vegetables are often found together in recipes, especially alongside cabbage – such as in borscht, stews, or salads. This classic combination creates depth of flavor and a balanced texture.
Radish, Parsnip, Celery – Lesser-Known but Equally Valuable
Radishes are spicy root vegetables that come in different varieties: black, white, green, and daikon. They are most often eaten raw in salads, appetizers, or vegetable mixes. Radishes have a bold flavor that invigorates and adds a spicy kick to dishes. They can also be sautéed, baked, or pickled. Daikon, for instance, is commonly used in Japanese cuisine. Parsnips are aromatic, cream-colored root vegetables that resemble carrots in shape but have a sweet and spicy taste. They are added to soups, vegetable broths, purees, and casseroles, or prepared separately as a side dish. Parsnips caramelize well in the oven and pair nicely with honey, aromatic herbs, and butter.
Celeriac (celery root) has a spicy taste and strong aroma. It is used in soups, vegetable mixes, salads, and purees. Celeriac can serve as a base for cream soups or as a substitute for potatoes in diet recipes. It can also be roasted or pan-fried as a steak. When combined with other vegetables, it creates a rich flavor base. These root vegetables are often cooked with onions, which enhance their natural sweetness and add aroma. This pairing is often used as a foundation for soups and stews.
Root Vegetables in Soups, Sides, Casseroles, and Salads
Root vegetables are essential components of many soups. In broths and cream soups, they create a nourishing and aromatic base. Carrots, parsnips, celery, potatoes, and beets complement meat and vegetable soups perfectly. They are often sautéed or stewed beforehand to enhance flavor and add color and density to the dish. In vegetarian soups, they can replace meat due to their texture and depth. In side dishes, root vegetables are served boiled, roasted, or fried. They can be cubed, sliced, mashed, or roasted whole. Popular options include roasted carrot, beet, celery, and parsnip mixes with olive oil and aromatic herbs. These sides are not only delicious but also visually appealing.
Root vegetable casseroles are hearty dishes that suit both everyday meals and festive occasions. Potatoes, beets, carrots, and celery pair well with eggs, cheese, cream, meat, or mushrooms. They are layered or mixed, seasoned, and baked to a golden crust. In salads, root vegetables can be used either boiled or raw. Familiar examples include vinaigrette, beet salad, Korean-style carrots, and fresh daikon mixes. They may serve as a base or complement to the dish, adding color, texture, and nutrients. These salads are beautifully complemented by beets, especially when combined with beans, nuts, or pickles. This classic pairing remains popular in many recipes.
Root Vegetables Around the World – Traditions and Interpretations
Root vegetables are widely used in global cuisines. In Eastern European cooking, they form the basis of borscht, soups, stews, and salads. In Poland, Ukraine, and Lithuania, carrots, beets, potatoes, celery, and parsnips are commonly used. Classic dishes include vinaigrette, borscht, braised cabbage with vegetables, and savory pies with vegetable fillings. In French cuisine, parsnips and celery are part of the aromatic mirepoix, which forms the base for sauces, soups, and broths. In the UK, parsnip, carrot, and potato-based casseroles, purees, and cream soups are popular. Beets are served with goat cheese or roasted in salads.
In Mediterranean countries, root vegetables are used in soups (such as minestrone), stews, seafood dishes, and pickles. In Lebanese cuisine, beets are often pickled with lemon juice and served with meat. In East Asia, daikon (a type of radish) is used as a base for soups, snacks, and pickles. It can be boiled, dried, fermented, or stir-fried. In Korea, pickled daikon (danmuji) is served with rice, noodles, or meat. Many of these dishes also include carrots, which add sweetness, color, and tender texture, blending well with other vegetables.
How to Choose, Store, and Prepare Root Vegetables
Root vegetables should be firm, without cracks, spots, softness, or sprouts. Carrots should be bright, smooth, and uncracked. Beets should be round or elongated, dark, and wrinkle-free. Potatoes should have no green spots, soft areas, or sprouts. Parsnips and celery should be heavy, pale, and have minimal side roots. Radishes should be firm and evenly colored. Store root vegetables in a cool, dark, well-ventilated place. Ideally, keep them in a box of sand, on a balcony, or in the vegetable drawer of the fridge. Avoid storing carrots and beets near apples – ethylene accelerates spoilage. Potatoes need dryness – excess moisture promotes rotting.
Before cooking, wash vegetables thoroughly, peel them, and cut according to the recipe. Some root vegetables, like beets or parsnips, are best boiled with the skin on to retain flavor and nutrients. Carrots and celery are well-suited for frying, baking, or boiling, while potatoes benefit from soaking in water after cutting to reduce starchiness. An ideal combination for many dishes is root vegetables with potatoes: they form a dense, balanced structure and pair beautifully with spices, herbs, cream sauces, or meat ingredients.